A Parent Guide to Grade 4 Mathematics
• Important math concepts in the 4th grade include
multiplying and
dividing with whole numbers and understanding fractions and decimals.
Based on national curriculum recommendations and reflecting Ohio Academic
Content Standards, the following describes some of the central mathematical
skills and understandings that students should acquire by the end of
fourth grade.
• Number and Operations
Representation and Place Value
1. Read, write, compare, and order numbers to one million; write numbers using
place
value (e.g., 2,068 is 2 thousands, 0 hundreds, 6 tens, and 8 ones)
2. Find all factors of any whole number through 50 and recognize some numbers as
prime (e.g., 3 is prime because it only has two factors, 1 and 3)
3. List the first ten multiples of a one-digit whole number and determine if a
whole
number is a multiple of a number (e.g., 3, 6, 9,12,15,18, 21, 24, 27, 30 are all
multiples of 3; 14 is not a multiple of 3)
4. Use mental math strategies to estimate and calculate with whole numbers
(e.g., 237 + 574 = ϑ , mentally think 200 + 500 = 700, 30 + 70 =
100, 700 + 100 =
800,
add the 7 + 4 or 11 to get a total of 811)
Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
5. Multiply any whole number by a one-digit number and a three-digit number
by a two-digit number
6. Divide numbers up to four-digits by one-digit numbers and by 10
7. Find the value of the unknown in simple mathematical equations,
such as find a if a ÷ 10 = 25 or find b if 120 ÷ b = 20
Fractions and Decimals
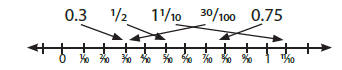
8. Locate fractions, mixed numbers, and decimals (tenths and hundredths) on a
number line ( e.g. find these on the given number line: 0.3, 1/2, 11/10, 30/100,
0.75)
9. Compare and order up to three fractions with
denominators 2, 4, and 8, and 3, 6, and
12, including mixed numbers (e.g. 5/8 < 3/4 )
10. Find and recognize equivalent fractions and explain why they are equal; know
decimal and fraction forms for tenths, hundredths, halves and fourths
(e.g., 3/10 = 30/100 = 0.3; 1/4 = 25/100 = 0.25 )
11. Read, write, interpret, and compare decimals through hundredths; relate
decimals to
money and place value (e.g., 0.14 is fourteen hundredths; $0.14 =14 cents)
12. Add and subtract fractions less than 1 with denominators of 2 through 12 and
100, where the denominators are equal or when one denominator is a multiple of
the other (e.g., 1/3 + 1/6 = 3/6 ); add and subtract decimals through hundredths
13. Multiply fractions by whole numbers; multiply and divide decimals up to two
decimal places by a one-digit whole number (e.g., 0.42 ÷ 3 = 0.14)
• Measurement
Units of Measure
14. Convert from one unit of measure to a larger or smaller unit of measure
(e.g., meters to centimeters, hours to minutes, feet to inches, ounces to
pounds)
15. Know and use formulas to find perimeter and area of squares and rectangles
(e.g., given a rectangle has an area of 10 square inches and one of the sides is
2 inches, find the missing dimension)
16. Measure using common tools (e.g., ruler, meter stick, thermometer) and
select
appropriate units of measure
• Geometry
Lines and Shapes
17. Identify and draw perpendicular, parallel, and intersecting lines and relate
angles
formed by these lines to right angles (e.g., square corners, 90°)
18. Identify basic two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and solids
(e.g., equilateral and right triangles, rectangular prisms and pyramids) and use
their relationships to solve problems
19. Move a shape by flipping, sliding, or rotating it; identify symmetry in
shapes
• Data and Probability
Represent and Solve Problems
20. Order a list of numbers, find the median and the range of values
21. Solve problems using data presented in tables and bar graphs
• Angle – a figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint
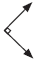
• Area – the number of square units that fit inside and cover the interior
of the figure with whole number side lengths
• Equilateral Triangle – a triangle with all sides the same length
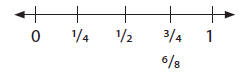
• Equivalent Fractions – expressions of the form a/b , where b ≠ 0, that name
the same
number (and so, are represented by the same point on the number line)
Example: 3/4 = 6/8
• Factors – positive whole numbers that divide a given number with no remainder
(e.g., factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12)
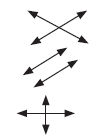
• Lines -
• Intersect – lines intersect if they have a point in common
• Parallel - lines that never meet
• Perpendicular – two lines that intersect and form
right angles
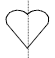
• Line Symmetry – the characteristic of a figure when it
can be
folded along a line so the two halves match exactly
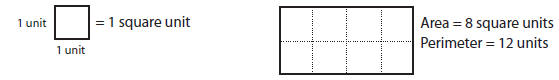
• Perimeter – the distance around the outside (boundary)
of a shape
Example: Find the area and perimeter of the rectangle
• Place Value - the amount represented by the position of
a digit in a number
(e.g., in 234, 3 is in the tens position and represents 3 tens)
• Prime Number – a whole number that has exactly two factors (whole number
divisors), 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7)
• Median – the middle value for an ordered list of data, half the data occur
above
the median and half the data occur below the median
Examples:
a) For five families with 1, 2, 2, 3, and 5 children,
the median number of children is 2
b) For six families with 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, and 5 children,
the median number of children is 2.5
• Mixed Number – a whole number plus a fraction (e.g., 3 ½ is a mixed number)
• Multiples of a Number – Multiplying a given whole number by another whole
number (e.g., multiples of 4 would be 4, 8, 12, 16,…. because 4 × 1 = 4, 4 × 2 =
8
4 x 3 = 12, and so on)
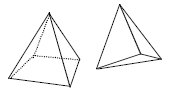
• Pyramid – a solid figure whose faces are triangles
that meet at a common vertex, with a polygon base
(e.g., triangle, rectangle)
• Range – the difference between the least value and the
greatest value in a list of
numbers (e.g., for six families with 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, and 5 children, the range is
4,
since 5 - 1 = 4)
• Rectangular Prism – a solid figure with six faces
(sides) that are all rectangles;
represented by a cereal box