Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
|
Objective: In this lesson you learned how to solve exponential and logarithmic equations. |
Course Number Instructor Date |
|
I. Introduction (Page 417) State the One-to-One Property for exponential equations. State the One-to-One Property for logarithmic equations. State the Inverse Properties for exponential equations and for logarithmic equations. Describe how the One-to-One Properties and the Inverse Properties can be used to solve exponential and logarithmic equations. Example 1: (a) Solve |
What you should learn How to solve simple exponential and logarithmic equations |
|
II. Solving Exponential Equations (Pages 418-419) Describe how to solve the exponential equation 10x = 90 . Example 2: Solve ex-2 - 7 = 59 for x. Round to three decimal places. |
What you should learn How to solve more complicated exponential equations |
|
III. Solving Logarithmic Equations
(Pages 420-421) Describe how to solve the logarithmic equation 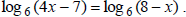
Example 3:
|
What you should learn How to solve more complicated logarithmic equations |
|
IV. Applications of Exponential and Logarithmic Equations (Pages 422-423) Example 4: Use the formula for continuous compounding, A = Pert , to find how long it will take $1500 to triple in value if it is invested at 12% interest, compounded continuously. |
What you should learn How to use exponential and logarithmic equations to model and solve real-life applications |
|
Homework Assignment Page(s) Exercises |
|



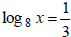 for
x.
for
x.